7 Ways to Guard Your Computer Against Malware
August 26th, 2019 by admin

An alarming number of companies underestimate the importance of malware prevention. Almost two-thirds of small businesses end up closing shop within half a year of a successful cyber attack. If you don't take the proper steps to protect your company's data, then you can fall victim to a similar fate.
Because most of us don't think twice about digital security, cybercriminals take advantage of this and find vulnerabilities in our systems to exploit. To fight against this, here are 7 ways to practice good malware prevention so your office network stays free of data breaches.
What Is Malware?
"Malware" is a portmanteau of the words "malicious" and "software." It is a type of program designed by cyber criminals who wish to infiltrate your system.
Most of the time, the purpose of malware is to gain access to your network so they can get sensitive or compromising data. They can then either blackmail you with the information, sell it, or perform fraud.
Types of malware include viruses, Trojans, spyware, and worms. There's also something called social engineering where criminals don't hack into your system. Instead, they trick you into revealing your private information by doing something like creating a fake login site.
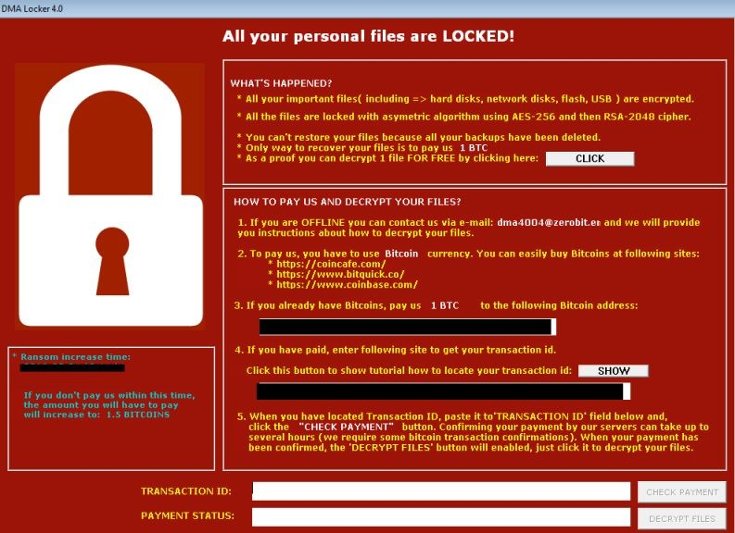
This is an example of the message you might get when your system is compromised with ransomware.
1. Install an Antivirus Program
As the name suggests, this program will keep your computer safe from viruses. Many of today's antivirus software come with additional features, such as real-time checks of links and attachments you click on.
As part of your malware prevention routine, you should run a full computer scan as soon as you install your antivirus program. You may have downloaded some malware previously and aren't aware of it. Any decent antivirus software should be able to find malware and remove it from your computer.
2. Install a Firewall
A firewall is what filters traffic that goes in and out of your network. Without a firewall, you leave all the computers on your network completely vulnerable to attacks.
Firewalls can come up with false positives sometimes, so it may be tempting to temporarily deactivate it so you can access legitimate websites. But never turn your firewall off; doing so for even a few minutes can be all it takes for malware to make its way onto your computer.
3. Create Strong Passwords
Cybercriminals will do brute force attacks where they'll continuously guess your password, usually through the use of a bot. This means that if you use regular dictionary words and obvious passwords (like your birthday), the chances of your password being compromised is significantly higher.
Try to use a combination of lowercase and uppercase letters, as well as numbers and symbols if the sites allow for it. Not only should you have a secure password, but you should use different ones across your accounts. It may easier to remember just one password on all websites, but as soon as it's compromised, that means cybercriminals basically have access to all of your accounts.
Since it can be hard to remember multiple complex passwords, you should consider using a password manager. This tool will remember all of your passwords securely and autofill them. All you need is a master password to access your bank of passwords.
4. Keep Your Software Updated
So you've installed an antivirus program and firewall, but your responsibilities don't end there. Developers find vulnerabilities in their software all the time, which is why they come out with updates and patches.
Those popups to update your software can be annoying, especially if you're in the middle of something. But you shouldn't delay them for too long. These vulnerabilities are what hackers use to breach your system, so plug up those holes as soon as you can.
The longer you wait to update your software, the bigger the chance a successful cyber attack will happen.
5. Don't Click on Links in Emails
Social engineering relies on cleverly done masquerading, which means you can find emails in your inbox that look legit. However, there's very small differences; differences you likely won't notice if you're just glancing at it quickly.
The main way hackers get malware onto your computer is through malicious links and attachments in emails. A good rule of thumb is to not click on links or attachments, even if you're 100% sure they're safe.
For links, type them in the browser bar yourself to ensure you're on the genuine site. For attachments, ignore them if you weren't expecting anything. If you were, double check with the sender through a text or call.
6. Use a Pop-Up Blocker
Many spoofed websites will have malicious pop-ups that install malware onto your device automatically. It'll be installed as soon as the pop-up loads, so you're practically helpless if you allow pop-ups.
With a pop-up blocker, you'll be protected from unwanted pop-ups loading and installing malware. Decent pop-up blockers give you the flexibility to allow pop-ups on your desired websites. This means you'll be able to adjust the settings to load pop-ups when you want it.
7. Work with a Cybersecurity Company
A cybersecurity company can add many layers of security to your network. While the above 6 tips can be useful in malware prevention, companies that specialize in cybersecurity can ensure your data is well protected.
Not only can they make sure data breaches are kept at bay, but they can also help back up your data in the event that you lose it all somehow. Plus, they can help you implement policies that comply with laws and regulations.
Keep Your Network Safe with Malware Prevention
By practicing good malware prevention, you can save your company from potential disaster. Make sure your employees understand how to fight malware; all it takes is one person for a successful attack to get through. Your business is only as strong as its weakest link, so good workplace education is vital in safeguarding your data.
If you need help managing your office's technology or want cybersecurity services, get in touch with us now.
Posted in: Solutions